OpenVAS (Open Vulnerability Assessment System)
Key Takeaways & Definition
- ● The Definition: OpenVAS (Open Vulnerability Assessment System) is a full-featured, open-source vulnerability scanner used to detect security loopholes, misconfigurations, and outdated software in a network.
- ● Core Context: It acts as the scanning engine for the broader Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM) solution.
- ● Key Use: Primarily used for Vulnerability Assessment (VA) to identify weak spots before hackers do.
Introduction to OpenVAS
In the world of cybersecurity, finding vulnerabilities manually is impossible given the millions of lines of code in modern networks. OpenVAS serves as an automated "search engine" for security flaws. Originally a fork of the famous Nessus scanner (before Nessus went proprietary/paid), OpenVAS remains the industry standard for free and open-source vulnerability scanning.
What is OpenVAS?
OpenVAS is a framework of several services and tools offering a comprehensive vulnerability scanning and vulnerability management solution. It is backed by a daily updated feed of Network Vulnerability Tests (NVTs), which are essentially "scripts" that check for specific bugs (like the WannaCry ransomware vulnerability or Heartbleed).
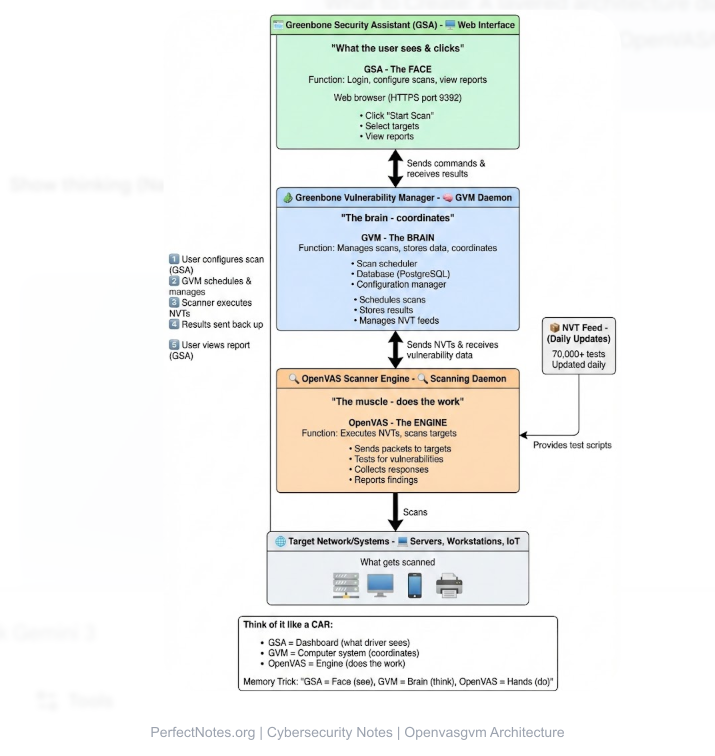
Architecture of OpenVAS (The GVM Framework)
OpenVAS is not just one tool; it is a collection of components working together, collectively known as GVM (Greenbone Vulnerability Manager).
OpenVAS Scanner
The core engine that actually executes the Network Vulnerability Tests (NVTs) against the target system. It sends packets and analyzes responses.
Greenbone Vulnerability Manager (GVM)
The "brain" of the system. It manages the configuration of scans, stores the results in a database (PostgreSQL), and controls the scanner.
Greenbone Security Assistant (GSA)
The "face" of the system. It is the web-based Graphical User Interface (GUI) where users log in, click "Start Scan," and view colorful reports.
OpenVAS Manager
(Legacy term) Now integrated into GVM, it handles the communication between the scanner and the user interface.
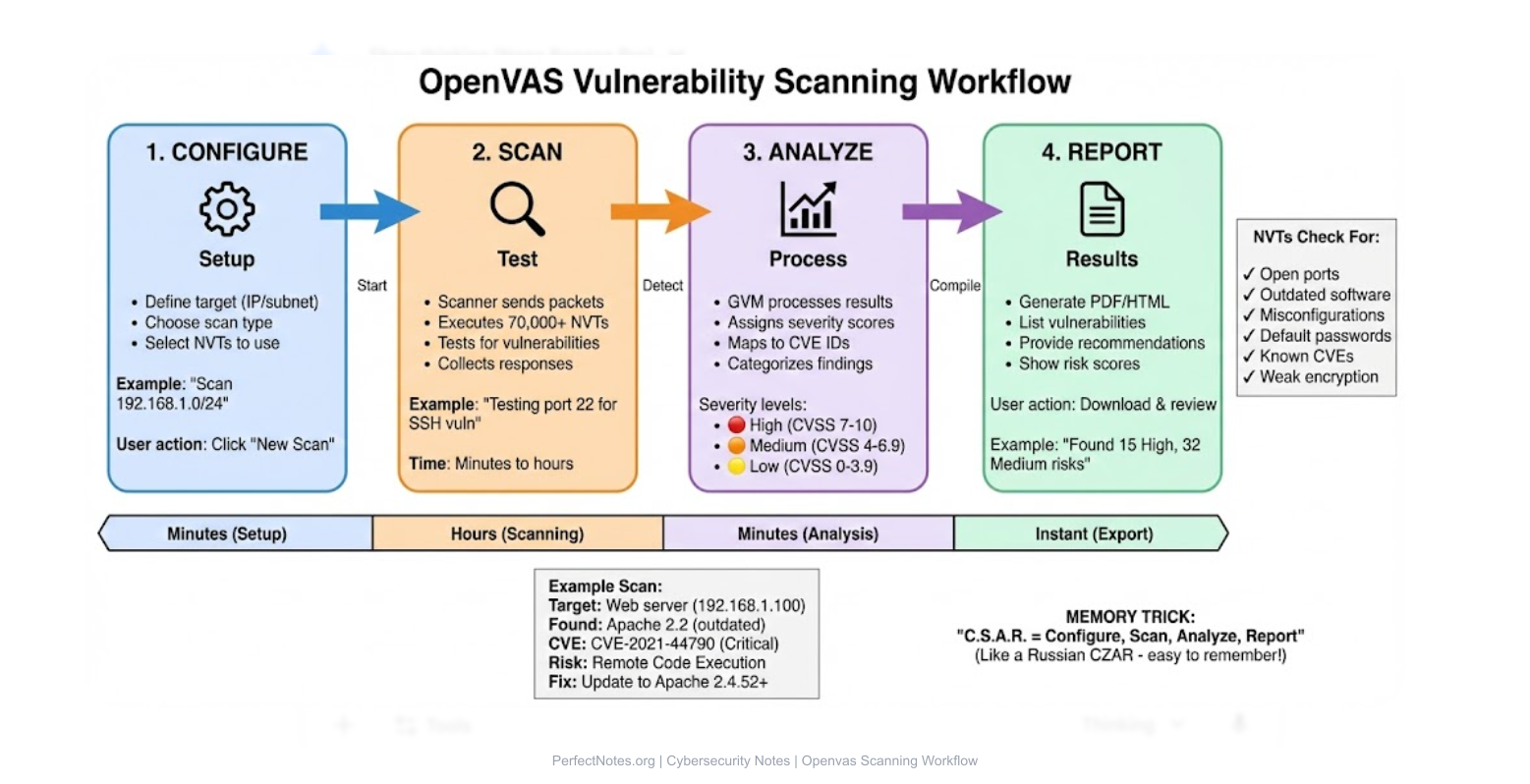
Working of OpenVAS
The scanning process follows a logical workflow:
Target Configuration
The user defines the IP addresses or subnets to scan (e.g., 192.168.1.10).
Scan Configuration
The user selects the type of scan (e.g., "Full and Fast," "Discovery," or "CVE-specific").
Vulnerability Detection
The Scanner executes thousands of NVTs. If a target responds in a specific way (e.g., displaying an old version number), the scanner flags it.
Report Generation
GVM compiles the findings into a PDF/HTML report, categorized by severity (High, Medium, Low).
Features of OpenVAS
- ✓Network Vulnerability Scanning: Detects open ports, weak services, and known CVEs.
- ✓Authenticated Scanning: If you provide login credentials, OpenVAS can log into the target machine to scan "inside" the system (finding missing patches like Adobe Reader updates).
- ✓Continuous Updates: The Greenbone Community Feed (GCF) updates the database with new threat signatures daily.
- ✓CVE and CVSS Support: It maps every finding to a standard Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) ID and assigns a Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) risk score (1.0 to 10.0).
⚠️ Limitations of OpenVAS (Exam Focus)
While powerful, OpenVAS has distinct drawbacks compared to paid tools:
- ● False Positives: It is notorious for flagging non-issues as risks (e.g., claiming a printer is a vulnerable server), requiring manual verification.
- ● Complex Setup: Unlike Nessus (one-click install), setting up OpenVAS/GVM requires Linux expertise and dependency management.
- ● Resource Heavy: A full scan can consume massive amounts of RAM and CPU, potentially slowing down the network.
Vulnerability Assessment Using OpenVAS
Network Vulnerabilities
Identifying unpatched Windows/Linux servers.
Service Misconfigurations
Finding servers allowing weak SSL/TLS encryption (e.g., SSLv3).
Outdated Software
Detecting old versions of Apache, PHP, or WordPress.
Weak Authentication
Checking for default credentials (e.g., admin/admin) on routers and IoT devices. This compromises the confidentiality of systems.
Comparison: OpenVAS vs. Nessus
Use this table to answer "Difference between..." questions:
| Feature | OpenVAS (GVM) | Nessus (Tenable) |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Free (Open Source). | Paid (Expensive Subscription). |
| Ease of Use | Difficult (Steep learning curve). | Easy (Polished UI). |
| False Positives | High (Requires manual checking). | Low (Very accurate). |
| Updates | Community Feed (Slight delay). | Professional Feed (Instant). |
| Best For | Students, Startups, Budget Labs. | Enterprises, Professional Auditors. |
Applications (Use Cases)
Enterprise Security Auditing
Regular monthly scans to meet compliance standards (ISO 27001).
Network Monitoring
Alerting admins when a new, unauthorized device appears on the network.
Compliance Assessment
Ensuring systems meet PCI-DSS standards (credit card security).
Academic Research
Used by students to learn vulnerability management without buying licenses.
Installation Overview
Linux-Based Deployment
OpenVAS is native to Linux. It comes pre-installed on penetration testing distributions like Kali Linux and Parrot OS.
Docker Deployment
Modern setups use Docker containers to isolate the GVM components, making updates easier.
Future of OpenVAS
The future lies in Automation. Integrating OpenVAS with DevOps pipelines (CI/CD) allows code to be scanned automatically before it is deployed. The shift is from "Periodic Scanning" to "Continuous Vulnerability Management."